Anyone searching for a primer on how to spot clever phishing links need look no further than those targeting customers of Apple, whose brand by many measures remains among the most-targeted. Past stories here have examined how scammers working with organized gangs try to phish iCloud credentials from Apple customers who have a mobile device that is lost or stolen. Today’s piece looks at the well-crafted links used in some of these lures.
KrebsOnSecurity heard from a reader in South Africa who recently received a text message stating his lost iPhone X had been found. The message addressed him by name and said he could view the location of his wayward device by visiting the link https://maps-icloud[.]com — which is most definitely not a legitimate Apple or iCloud link and is one of countless spoofing Apple’s “Find My” service for locating lost Apple devices.
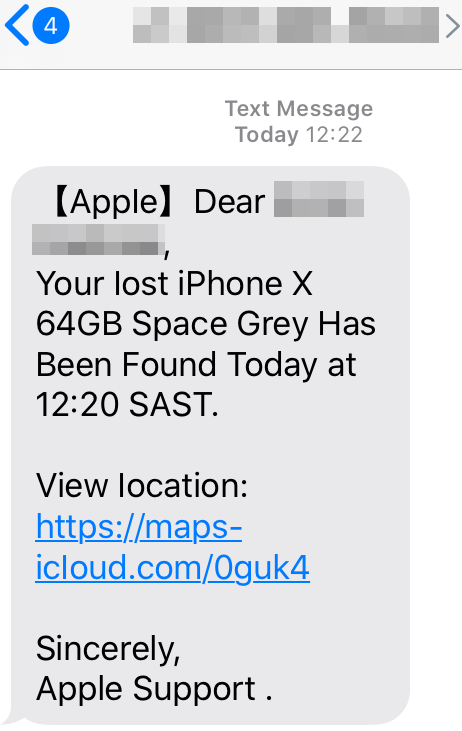
While maps-icloud[.]com is not a particularly convincing phishing domain, a review of the Russian server where that domain is hosted reveals a slew of far more persuasive links spoofing Apple’s brand. Almost all of these include encryption certificates (start with “https://) and begin with the subdomains “apple.” or “icloud.” followed by a domain name starting with “com-“.
Here are just a few examples (the phishing links in this post have been hobbled with brackets to keep them from being clickable):
apple.com-support[.]id
apple.com-findlocation[.]id
apple.com-sign[.]in
apple.com-isupport[.]in
icloud.com-site-log[.]in
Savvy readers here no doubt already know this, but to find the true domain referenced in a link, look to the right of “http(s)://” until you encounter the first forward slash (/). The domain directly to the left of that first slash is the true destination; anything that precedes the second dot to the left of that first slash is a subdomain and should be ignored for the purposes of determining the true domain name.
For instance, in the case of the imaginary link below, example.com is the true destination, not apple.com:
https://www.apple.com.example.com/findmyphone/
Of course, any domain can be used as a redirect to any other domain. Case in point: Targets of the phishing domains above who are undecided on whether the link refers to a legitimate Apple site might seek to load the base domain into a Web browser (minus the customization in the remainder of the link after the first forward slash). To assuage such concerns, the phishers in this case will forward anyone visiting those base domains to Apple’s legitimate iCloud login page (icloud.com).
The best advice to sidestep phishing scams is to avoid clicking on links that arrive unbidden in emails, text messages and other mediums. Most phishing scams invoke a temporal element that warns of dire consequences should you fail to respond or act quickly. If you’re unsure whether the message is legitimate, take a deep breath and visit the site or service in question manually — ideally, using a browser bookmark so as to avoid potential typosquatting sites.
Anyone searching for a primer on how to spot clever phishing links need look no further than those targeting customers of Apple, whose brand by many measures has emerged as the most targeted. Past stories here have examined how scammers working with organized gangs try to phish iCloud credentials from Apple customers who have a mobile device that is lost or stolen. Today's piece looks at the well-crafted links used in some of these lures. by: BrianKrebs via https://www.AiUpNow.com/