After demonstrating scale, growth and financial improvement, one founder of a two-year-old agritech startup based in India told me that he’s now confronting a new challenge: Unlike his peers in edtech, fintech or e-commerce, there are very few investors he could approach for raising funds, he told TechCrunch, requesting anonymity. He suggested that a startup of a similar scale solving a similar problem would have little issue raising more than $50 million. But for his startup, seeking a $10 million financing round has proven very elusive in recent quarters, he said.
The story of this startup counters the narrative that fundraising for Indian startups has become easier than ever and that young firms have access to abundant capital from the market. India’s startup ecosystem raised about $14.5 billion in fundraises last year, beating its previous best of $10.6 billion in 2018, according to research firm Tracxn. But a closer look reveals that much of the capital went to a handful of late-stage startups, a trend that continues today.
In the first half of 2020, early-stage startups participated in 577 rounds to secure $1.84 billion, Tracxn told TechCrunch. That figure is the lowest the Indian startup ecosystem has seen in years. In the second half of last year, early-stage startups participated in 752 rounds to raise $3.03 billion, and in the first half of 2019, they raised $2.7 billion from 856 rounds. Series A and Series B startups are not immune to this trend either: In Q1 and Q2 2020, these startups raised $1.55 billion from 186 rounds, down from $2.69 billion from 254 rounds in the second half of last year and $2.37 billion from 279 rounds in the first half of last year, according to Tracxn. Once again, the first half of 2020 was the slowest in years for this segment.
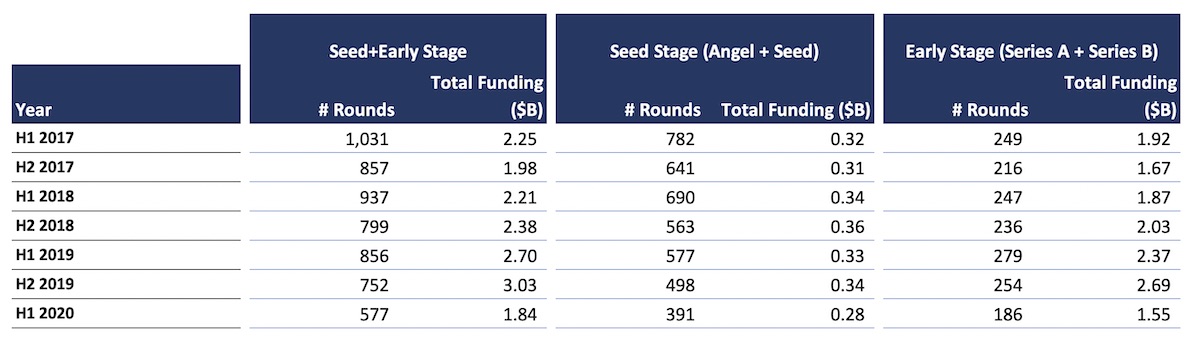
Funding received by startups in India. Image Credits: Tracxn
Extra Crunch spoke with several VCs to understand how they were tackling this gap. We granted some of them the freedom to speak anonymously. At TechCrunch Disrupt 2020, Karthik Reddy, co-founder of Blume Ventures, India’s largest VC firm, acknowledged the gap, adding that, “There’s an artificial skew toward unicorns and chasing the unicorns.”
via https://www.aiupnow.com
Manish Singh, Khareem Sudlow
